
MARINE INSURANCE SERVICES
62 Commonwealth Road, Barrie,
Ontario, L4M 0C9, (705) 728-7437, FAX (705) 730-0518
C43 SPECIALTY LINES
SUMMARY NOTES
2001
STUDY 1 GLASS INSURANCE
POLICY COVERAGE: Most Glass now insured under All Risks forms--not insured separately. Most Glass losses are for amounts less than deductible. Also, inspection/underwriting glass is expensive & premiums generated low causing recent decline in separate glass coverage.
Insuring Agreements:
|
GLASS POLICY |
ALL RISKS PROPERTY POLICY |
|
Covers All Damage to insured glass, lettering, ornamentation from accidental breakage during policy period. |
Excludes loss/damage to Exterior Glass except for Named Perils. |
|
Broader Coverage than All Risks form. |
Covers Riot/Vandalism/Malicious Mischief. |
|
|
Excludes Theft/Attempted Theft. |
5 Exclusions:
1 Loss/Damage by Fire (Cover Purchased Separately).
2 Common War Perils.
3 Loss/Damage during Construction, Alterations or Additions to described
premises other than normal repair/maintenance.
4 Loss/Damage while premises Vacant/Unoccupied 30+ days to the knowledge of
Insured.
5 By-Laws exclusion.
STANDARD CONDITIONS (GENERAL CONDITIONS IN QUÉBEC):
1 Declarations: Binds Insured to agreements & representations.
2 Ownership of Property Insured: Insured is not required to own glass or be
liable for its loss. Some leases make tenants responsible for glass
(insurable interest).
3 Changes: No changes to contract without Insurer’s written consent
(telling the agent of changes is not enough).
4 Assignment: Change of interest permitted by endorsement with Insurer’s
written consent (with exceptions e.g. death, bankrupt, insolvent).
5 Inspection: Insurer may inspect premises at any reasonable time.
6 Payments & Replacements: Usually glass replaced immediately, not just
paid (paying privilege rarely exercised). Insurer pays glazier
instead. Broken glass is salvage for the Insurer. Removal is
covered.
7 Notice of Breakage: The Insured must promptly give written notice of breakage
with full particulars of the loss to the Insurer (sworn proof of loss if
required) and prevent further damages.
8 Other Insurance: If more than 1 policy applies, the loss is pro-rated.
9 Subrogation: Insurer can recover damages from the responsible party up
to the cost of repairs.
10 Reinstatement: Payment of a claim does not automatically cancel the
policy or reduce the amount of insurance.
11 Cancellation--Termination:
By Insurer: With at least 15 days written notice by registered mail, 5 days
personally delivered, excess Premium returned pro-rata.
By Insured: At any time on request, excess Premium returned Short Rate, subject
to minimum retention.
SCHEDULE: If a schedule is included, clear flat plate/crystal/double
diamond/sheet glass covered only, other glass excluded unless described (or
unless coverage is Blanket--All Exterior Glass). Schedule Includes:
1 Item Number
2 Location Number
3 Number of Plates
4 Dimensions of Plates (Height X Width, cm)
5 Location of Plates (Interior or Exterior)
6 Description
7 Limit of Insurance (Optional)
8 Premium
UNDERWRITING/INSPECTION OF RISKS: Broker or Agent selects risks & determines premiums.
BROKER’S/AGENT’S ASSESSMENT: Measurements of each pane rarely taken. For rating, the broker may calculate the total linear footage. The broker should note the condition of frames, plates, and determine cause of breakage (e.g. building settling), and repairs should be done before insuring.
WINDOW DRESSING: Congested show windows cause frequent breakages from inside.
NEED TO INSURE ALL GLASS: Avoid selection, insure at least all exterior
glass; poor underwriting to insure only
large glass front.
LOSSES: Obtain glass loss experience information before insuring. Some causes of loss are difficult to determine.
LOCATION: Rates higher for congested areas and cities (vandalism), especially for busy intersections (unknown cause losses higher).
USE OF PREMISES: In the past, some uses were subject to higher risk, (e.g., auto. showrooms). Today, occupancy does not affect rates, except for: apartment houses, churches, hospitals, clubs, public libraries, govt./municipal/educational buildings (other than schools).
PREMIUM COMPUTATION:
1 IAO Casualty Manual--Glass Part.
2 75 % of all glass is Grade Floor Exterior/Sheet Glass, area-rated, this rate
is subject to a class multiplier and a territory multiplier. Rated by
Size of Glass (Height X Width + 1 inch each side), if irregular shaped, then
measure maximum length X width.
3 Other types of glass cost-rated. Estimated replacement cost X class
multiplier.
4 Apartment houses may be flat-rated, 10+ suites, blanket coverage on all
exterior glass, flat premium. Excludes cost-rated, multiple-set glass,
lobbies. Rates greater as # suites greater.
|
AREA-RATED |
COST-RATED |
|
Clear flat plate, crystal, double diamond, sheet |
Bent glass |
|
Clamped |
Glass building, mounted bricks |
|
Show cases, wall cases |
Hermetically sealed units 2+ plates |
|
Awnings, canopies, roofs, skylights |
Laminated, tempered |
|
Chipped |
Leaded, memorial, jeweled, embossed cut, stained, |
|
Counter, desk, table top |
Lettering, ornamentation, tapes, foils |
|
Shelves |
Flat mirror |
|
Wire glass |
Pavements, floors |
|
Sanded, ribbed, Luxlite, fluted, rolled prismatic, other fancy glass |
Signs, screens |
|
Golden, solex |
Structural glass |
|
|
Enclosed mall storefronts |
|
|
Vitrolite, carrara, opalite |
STUDY 2 SURETY BONDS
DEFINITIONS:
1 Surety Bonds: Guarantees that 1 party’s obligations to another will be
fulfilled; associated with insurance and using same distribution system. Acts
as security for another contract, indebtedness, or promise of faithful
conduct. Suretyship is contingent security.
2 Suretyship: Service rendered by a Surety.
3 Bond: Written contract under seal; evidence of a Surety’s guarantee; 3
parties:
Principal: One on whose behalf bond issued (employee).
Obligee: One to whom bond payable (beneficiary, employer).
Surety: One who indemnifies (guarantor).
4 Bond Penalty: Amount $ Surety will pay should the Principal default.
|
INSURANCE |
SURETY |
|
2 Party Contract |
3 Party Contract |
|
Duty of Utmost Good Faith |
Disclosure: as in ordinary contract law |
|
Cancellable |
Non-Cancellable |
|
Calculates Premium Based on Losses |
No Loss Anticipated, Fee for Service |
|
Involves Transfer of Risk |
No Transfer of Risk |
|
No Reimbursement from Insured |
Principal Reimburses Surety |
Corporate Suretyship: A company (rather than a person) provides these services (as corporations are more financially stable). Most Sureties are Insurers.
The Construction Industry: 80% of all surety premiums. 2 types of
projects:
1 Building: High-rises, shopping centres, govt. buildings; directed by
architects.
2 Engineering: Roads, bridges, sewers, waterworks, docks; heavy civil
engineering.
Contractors (main clients of Sureties) contract with owner for construction work; 3 types: general (buildings), engineering (heavy construction, e.g., roads, bridges), specialty (plumbing, heating, electrical, plastering, roofing, etc.). Contractors may hire Subcontractors.
Joint Ventures: For very large jobs, several corporations join together to acquire special skills and experience, pool financial resources, and spread the risk. Formal partnership or separate corporation formed.
Tendering: A formal call to interested parties to submit bids to do the
construction work for the described project.
Tender Call published in construction newspapers.
Construction Bonds: Most common; Include bid bonds, performance bonds,
labour & material payment bonds, and maintenance bonds. Makes the
contract between Principal & Obligee part of contract between Surety &
Principal.
1 Bid Bond: Assures owner that contractor is serious and operating in good
faith, able to complete the job, must enter into contract with owner if bond accepted,
and firm and competitive contract price. If contractor fails to enter
into contract, then owner will be compensated for difference in cost of hiring
next lowest bidder.
2 Agreement to Bond (Consent of Surety, Bid Letter): May accompany or substitute
for a bid bond. Surety agrees to furnish necessary bonds if accepted.
3 Performance Bond: Assures owner of project’s completion, up to amount of
bond. Maintenance Clause--includes 1 year period to correct defects not
discovered right away.
4 Labour and Material Payment Bond: Protects suppliers of labour & material
used by general contractor, in case contractor fails to pay them. If
contractor defaults, then owner receives funds in trust to pay to suppliers
(owner here is a trustee). Claimants have a direct contract with general
contractor (sub-contractors). Broad Form Payment Bond: Claimants do not
need direct contracts with general contractor.
5 Maintenance Bond: If maintenance period longer than 1 year (not covered by
Performance Bond); covers defective material & workmanship.
Other Contract Bonds:
6 Supply Bond: Required when owner requests general contractor to furnish
materials/components within certain time.
7 Subcontract Bond: Between general contractor & subcontractor; bond should
be very similar to the contractor’s bond to minimize risk to the Surety, and
limited to the subcontractor’s obligations.
Completion of Obligation: When job completed, Surety should obtain a
release.
|
Bond Type |
Purpose |
Principal |
Surety |
Obligee |
|
Bid Bond |
Pre-qualify, Weed out speculators |
Enter Contract, Give Security |
Pay difference, Obtain another bidder |
Take best offer |
|
Performance Bond |
Guarantee Contract Conditions |
Promptly and faithfully perform contract |
Remedy default, Complete |
Make regular payments to principal |
|
Payment Bond |
Pay for unpaid labour and material |
Make payments to all claimants for labour and material |
Pick up principal’s obligation to make payments |
Act as trustee for unpaid subtrades |
|
Maintenance Bond |
Guarantee work done is free from debts |
Repair or replace any defective work |
Remedy default by paying for any defects |
Report defects |
Underwriting: Surety should examine information about the applicant before
providing bond, regarding:
|
GENERAL |
OPERATIONAL |
FINANCIAL |
|
Reputation & experience |
Management |
Banking relationship |
|
Subsidiaries & other related companies |
Employees |
Credit record |
|
References |
Business plan |
Financial statements |
|
Prior sureties |
Performance record |
Cost & billing figures |
|
|
Bid analysis |
|
|
|
Jobs in Progress |
|
Rating: Premium is a fee for services, annual, based on contract price (not bond penalty amount). Contract bond rates depend on relationship of bond penalty to the contract price (50% bond costs less than 100% bond). First year premium fully earned (no partial refund if job completed in less than 1 year). If not completed in 1 year, then bond is renewed & extra premium charged.
Alternative Rates: For large/long-term contracts. 2 year term, combined rate (performance & payment bonds). Premium is adjusted upon final contract price. Premiums (& broker’s commissions) reduce with time.
Surety Credit Underwriting: Surety will appraise contractor’s ability to pay
back borrowed funds, unsecured basis (no collateral), uses contract funds &
indemnity agreements as a safety net. The ‘C’s of Credit Analysis:
Character: Integrity/honesty of person, dedication, will to succeed.
Capacity: Ability to complete the job. History, experience,
structure.
Capital: $ required, balance sheet will indicate equity position.
Conditions: Current economy, environment in which Principal functions.
Communication: Dialogue between Principal & Credit Underwriter.
Underwriting International Projects: Normally, an arrangement (Fronting Agreement) is made with a company licenced to work in that country (usually USA). Bond is issued in Fronting Company’s name. A foreign Surety will also be involved. Along with usual underwriting considerations, also take into account differences in currency, foreign economy, cultural environment, foreign claims personnel to handle default, geography, climate, language, availability of materials, productivity/skill of local labour force, medical services, laws & customs.
Underwriting Joint Ventures: Along with usual underwriting considerations, also evaluate paid-in-cash capital, joint venture agreement, division of responsibilities, ‘joint and several’ obligations, accounting records, contingencies, appropriateness of the alliance (combine strengths not weaknesses).
STUDY 3 MISC. SURETY BONDS
Bond Wordings: Wordings governed by law; term fixed or continuous until cancelled; guarantee clause (bond amount); non-cumulative; discovery period.
Licence/Permit Bonds: Needed for government (Obligee) to issue a licence to an individual for Private Investigator, Security Guard, many other purposes (of risk to public welfare). Bonds protect public against incompetence, misrepresentation, fraudulent dealings, BI/PD; ensure compliance of laws. Some are Forfeiture Bonds (total amount stated is paid in event of loss, regardless of amount of loss, e.g., security agents).
Customs and Excise Bonds: Continuous, Renewable, Cancelable by Surety with
60 days notice to Dept. National Revenue. Government (Obligee) guarantees
taxes/duties paid by Principal.
1 Canada Customs Bond (1991) multi-purpose, includes Customs Broker Licencing,
obligations, term, cancellation.
2 Customs Warehouse Bond for storing imported goods.
3 Inward Remission Order Bond for products destined for sale outside
Canada. Relieves Customs tariffs for goods that will not stay here
(ensures such tariffs will be paid if goods are not exported).
4 Alcohol Bond relieves excise duty for users of pure/denatured alcohol (e.g.,
Perfume mfg.). Alcohol held in bond, locked, cannot be opened without
official of Dept. National Revenue. This bond protects against losses
where an amount is lost and the user must pay taxes.
5 Wholesalers Tax Bond not required since GST (1991) unless non-resident sells
products in Canada.
Court Fiduciary Bonds: Security for court costs, release liens, probate &
bankruptcy needs. Effected at short notice; released by letter from
lawyer to Surety.
6 Litigation Bond: Protects defendant from loss if final decision adverse.
7 Appeal Bond: Ensures judgment of court & interest/costs will be paid if
appeal fails.
8 Security for Costs Bond: Security for costs incurred in litigation; ensures
costs will be paid (financial guarantee); bond amount set by judge (no
relationship to value of suit).
9 Replevin Bond: Recovers property belonging to plaintiff but that has
wrongfully been taken away. Obligates plaintiff & Surety to return
property, or pay its value plus damages for loss of use if plaintiff is shown
to not be legal owner.
Builder’s, Construction, or Mechanic’s Lien Bond: Attachment on a property by creditors to protect themselves against financial indebtedness of owner. It is a registered interest in property, with the right of the creditors to be paid out of the sale of the property. Lien can be discharged by filing this bond; payment is guaranteed.
Fiduciary Bonds: Fiduciary is a person to whom the administration of something is entrusted for the benefit of another. Bond protects financial interests of other person who is relying on the Fiduciary.
Administration Bonds: Guarantees faithful performance of the administration
of a deceased person’s estate. There is no premium or term (Surety can
have separate annual premium). If a person dies without a will,
beneficiaries appoint Administrator who files bond, pays debts and divides the
rest. If estate is insolvent (debts exceed assets) then funeral paid
first, followed by administration costs, all other debts paid pro rata, no
distribution to heirs. Bond held by and cancellable (only) by court.
i Executors Bond: When there is a will with executor named, handling of estate
directed by will, not the law.
ii Administrator With Will Annexed: When there is a will but executor not
named/refuses/unable.
iii Administrator De Bonis Non: When 1 executor replaces another.
iv Ancillary Administrator: When out-of-province property involved.
Guardians & Committees: Guardian is appointed by court to handle the
administration of property of a minor. Committee is appointed by court to
handle affairs of one who is incapable.
Trustees in Bankruptcy: Trustee appointed by court when individual, firm, or
corporation files for bankruptcy; trustee is responsible for the liquidation of
assets.
Trustee Licence Qualifying Bond: Federal Bankruptcy Act regulates these
trustees; guarantees trustee will follow rules & conditions of Act.
Individual Estate Bond: For recovery of creditor’s interests.
Lost Document Bonds (Bond of Indemnity): Security for lost/mislaid/destroyed
document, security, or instrument (e.g., proof of ownership). Bond
guarantees that owner of lost instrument will reimburse issuer if later
cashed. Bond terminates when originals found. Single premium paid
(not annual). 2 types:
1 Fixed Penalty: Fixed $ amount, used if security has fixed value, e.g.
certified cheque; rate per $1000.
2 Open Penalty: Unlimited $ amount, used if security subject to price
fluctuation, e.g. stock certificate; higher rate, from value at date of issue.
Financial Guarantee Bonds: Guarantees repayment of a loan or payment of
rent.
1 Completion Bonds: For construction projects; not tied to the construction
contract; protects loan advanced to project; lending institution usually
included as dual obligee under performance bond to avoid completion bond.
2 Land Sub-Dividers Bonds: Guarantees land purchaser that certain services
(water main, sewer, etc.) will be installed.
Underwriting Misc. Surety Bonds: 3 Steps:
1) Identification of the Risk: Nature & Extent of Principal’s
Obligation. Examine governing law or terms & conditions of contract.
2) Examine Terms of Obligation: Wording of Agreement--Determine Term (Fixed or
Indefinite), Cancellation provision (notice), rights of obligee/3rd parties,
period allowed to bring suit. Greater Obligation = greater Risk to Surety.
3) Determine the Principal’s Qualifications (Character, Capacity, Capital).
Underwriting Considerations:
i If applicant’s financial strength questionable, Surety may accept a
third-party indemnitor.
ii For hazardous risk, Surety may require Cash Collateral.
iii Surety can also insist on Joint Control of cash/property administered.
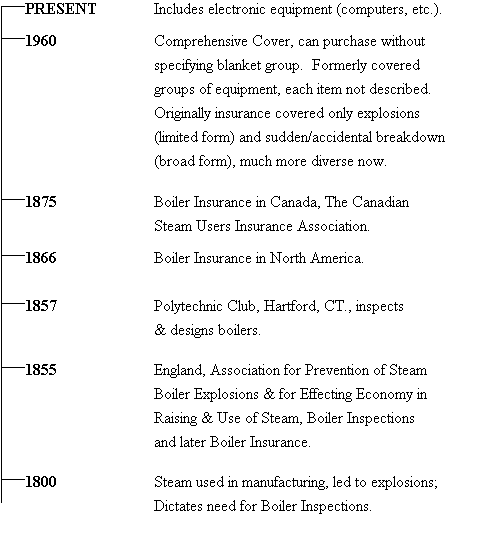
STUDY 4 BOILER & MACHINERY INSURANCE
HISTORY OF BOILER & MACHINERY INSURANCE
COVERAGES:
|
PROPERTY POLICY |
BOILER & MACHINERY POLICY |
|
Lightning |
Lightning |
|
Furnace Explosion |
Explosion/Bursting/Rupture of Boilers/Pressure Vessels over 15 psi |
|
|
Mechanical Breakdown |
|
|
Electrical Arcing |
|
|
Electrical Failure |
Overlapping Coverages: Where Boiler & Machinery Insurance overlaps Property Policy (e.g. damage from lightning), Use Agreement of Guiding Principles (Property Insurance) IBC-Section D to determine proportion of payments (Joint Losses). Where Boiler & Machinery Insurer & Property Insurer disagree about respective liability, Use Agreement Respecting Disputed Losses between Property Insurance and Boiler & Machinery Insurance Policies, at Insured’s request. Insurers bound by both agreements if signatories to them.
Inspection/Loss Prevention: Periodic inspections are required by law--by inspectors with certificate of competency; some provinces have Insurers do inspections. Loss prevention is very stressed in this field.
Insuring Agreement: Pays for loss from Accident to Object in use or ready
for use at an insured location for:
Damages to Object
Damages to property of Insured
Damages to property of others in Insured’s care/custody/control for which
Insured legally liable
Object: Pressure/Mechanical/Electrical/Electronic Equipment owned,
leased, operated, or controlled by Insured, unless specifically excluded, 2
Parts:
1) Pressure Equipment: Includes accessory piping, subject to internal (not
static) pressure; cracking is most common today. Expendable parts &
certain piping excluded. Ovens, Stoves, & Kilns, excluded (covered by
Property Policy).
2) Mechanical/Electrical Equipment: machines/apparatus for generation,
transmission, utilization of mechanical or electrical power, not including
elevators, escalators, cranes, hoists, vehicles, power shovels, excavators,
draglines, mobile equipment, ovens, stoves, kilns, furnaces, conveyor
belts. However, electrical equipment used with these items is an Object.
Production Machines: Equipment that handles materials rather than
generate/transmit/utilize power; excluded - added for extra premium.
Driving or controlling mechanism of Production Machine is covered.
Electronic Equipment: Excluded - Added for extra premium.
Comprehensive Cover: All parts of Equipment covered.
Blanket Cover: Parts of Equipment assigned to groups covered.
Accident: Fortuitous/Sudden/Accidental breakdown of an object, must result in simultaneous physical damage to Object of such a nature that requires repair or replacement; no gradual breakdowns. Excludes depletion, deterioration, corrosion, erosion, wear/tear, vibration, misalignment, leakage, breakdown of supporting structure, safety/protective device, cracking of gas turbine.
Exclusions: 3 types of losses:
1) Losses not intended to be covered by Boiler & Machinery Insurance (e.g.
Nuclear Incident).
2) Losses covered by Property Policy (e.g., Fire).
3) Losses normally not covered but provided by endorsement (e.g., By-Laws
Coverage).
Conditions: Not statutory like Property Policy, similar conditions;
unique to Boiler & Machinery Insurance:
1) Limit per Accident (per Occurrence).
2) Basis of Settlement: Insurer pays lesser of cost to repair/cost to replace.
3) Automatic Coverage: Newly acquired locations covered with 90 days notice and
extra premium.
4) Inspection: Insurer can inspect at any reasonable time.
5) Suspension: Insurer can suspend cover without waiting period on
discovery of dangerous condition. Reinstated by endorsement. Pro
rata return of premium while suspended.
6) Cancellation:
By Insured: At any time, 25% short rate penalty.
By Insurer: 15 days notice by registered mail, pro rata return of premium.
Extensions: Other Standard Coverages:
1) Expediting Expenses: Reasonable extra costs to make temporary repairs or
expedite repair (overtime wages, rush transport).
2) Ammonia Contamination: Covers damaged property when an Accident to an Object
causes an Ammonia spill (common refrigerant).
3) Water Damage: Covers property damaged by water from an Accident to an Object
(some types of pipes only), if excluded in Property Policy.
STUDY 5 BOILER & MACHINERY INSURANCE-- INDIRECT COVERAGES
Indirect Loss: From Accident to Object (not insured peril); Indirect loss can sometimes be greater than Direct loss. Coverage available for Business Interruption, Extra Expense, Consequential Damage losses, added by endorsement for extra premium.
Business Interruption: For interruption of business caused solely by
Accident to Object in use or connected ready for use at an insured
location, subject to specified limit.
2 Aspects:
Reduction in Earnings.
Expense necessarily incurred to reduce business interruption loss.
Conditions:
Limit of Liability (Amount of Insurance, Limit of Loss): Maximum amount per
Accident (in addition to Direct Damage limit).
Commencement of Liability: Begins 24 hours before Insurer receives notice of
Accident or at time of Accident, whichever later; prompt notice is to Insured’s
benefit.
Resumption of Business (Resumption of Operations, Reduction of Payment,
Reduction of Loss): Insured must begin within reasonable time to make up lost
business by all means reasonably possible and reduce/avert interruption of
business at the location.
Waiting Period: If stated, Insurer not liable during period, affects
Commencement of Liability period as well.
Deductible: $ value stated or Average Daily Value (ADV), reduces Insurer’s
liability.
Adjustment of Premium: Premium based on estimated future earnings; if Insured
paid too much he can file Report of Values within 1 year and a proportion of
premium is returned, no return if a loss occurred (premium fully-earned).
Exclusions:
Losses excluded in the Direct Damage policy, except Indirect Damage losses.
Losses that occur during time when business would not have continued without
such accident.
Losses from Insured’s failure to resume business with due diligence &
dispatch.
Business Interruption Forms, 5 Types:
1) Gross Earnings: Covers reduction in gross earnings from business
interruption by Accident to an object, less non-continuing expenses.
Gross earnings is the sum of the total net sales value of production, plus
total net sales of merchandise, plus any other earnings from operations, minus
cost of raw stock used in production and supplies consumed in production,
merchandise sold, services purchased, and ordinary payroll.
Coverage ends when insured property rebuilt/repaired/replaced.
Exclusions:
Damage to finished stock.
Damage from strikers or others interfering with rebuild, repair, replace,
resumption of business.
Fines/Breach of Contract/Late Orders/Other Penalties.
Cancellation of Lease/Licence/Contract/Order.
Consequential/Remote Losses.
Coinsurance: Usually 80% of gross earnings must be maintained.
2) Loss of Profits: Loss from reduction of profits from Accident to Object.
Gross Profits is the sum of net profit and insured standing charges.
Net Profit is the net trading profit less standing charges and other charges
like depreciation.
Standing charges are operating expenses that continue (fixed) or may continue
(semi-variable) in event of shutdown of business (total or partial).
Coverage ends when Insured’s gross profit returns to normal or indemnity period
ends (usually 12 months), whichever first.
Coinsurance: None stated; will be penalized proportionately for
underinsurance (Average Provision).
3) Actual Loss Sustained: Loss from reduction of net profits on business
from Accident to Object, plus fixed charges and expenses.
Coverage ends when business is resumed.
Additional Exclusion: Loss from lease/licence/order lapsed from Accident.
Coinsurance: Insured must specify annual value of expected loss, Insurer
liable for proportion with respect to this value, estimated fixed charges, and
net profit.
4) Rent or Rental Value: Loss from reduction in gross rent or rental value
from Accident to Object, making it untenantable, less continuing expenses.
Coverage ends when rebuilt/repaired/replaced, business resumes, or 12 months.
Daily Indemnity (maximum $ per day) and Maximum Limit for Loss.
Underinsurance is common; Insureds choose low daily indemnity for a lower
premium; form does not respond to fluctuations in business (seasons).
Additional Exclusion: Loss from suspension/lapse/cancellation of lease, licence
or order.
Coinsurance: None stated; reduced proportionately if underinsured.
5) The Valued Form: Flawed, rarely used now. Insured not required to report values. Pays Daily Indemnity $ amount for Total or Partial Prevention of Business. Insureds tend to underinsure. This form does not respond to business fluctuations.
Extra Expense: All Business Interruption forms carry some extra expense
provision, if expense reduces loss. Additional coverage is available for
expenditure as some Insureds need to continue operations even if costs exceed
income. Additional cost to conduct business during restoration (greater that
the normal costs without Accident).
Coverage: Extra expense required to continue as nearly as practicable the
normal operation of business after Accident to Object. Coverage ends when
business resumed.
Additional Exclusion: Licences, etc. as above.
Coinsurance: None stated.
Consequential Damage: Loss to specified property that spoils due to lack of
power, light, heat, steam, or refrigeration from Accident to Object; specified
property can be property of others for which Insured legally liable.
Resultant Damage cover also available (broader).
Conditions: Deductible and Reduction of Payment.
Additional Exclusions: Depreciation losses.
Business Interruption Options:
Ordinary Payroll: Excluded from Gross Earnings, Loss of Profits, Actual Loss
Sustained forms (non-continuing expense). Cover added for extra premium;
for specified period 90-365 days. Coverage ends when business resumed.
Waiver of Coinsurance: Waives coinsurance clause in Gross Earnings, Actual Loss
Sustained, Rent/Rental Value forms. Average provision may be suspended on
Loss of Profits form. Available for extra premium; certified values required.
Auditors Fees: For services in settling business interruption claim, cover for
fees added; services must be authorized by Insurer; a sublimit applies.
Professional Fees: Broader coverage than Auditors Fees, includes lawyers,
accountants, etc; applies also to indirect losses.
Service Interruption: Cover for indirect losses from Accident to Object owned
by Public Utility or other service to Insured; equipment must be within 300
metres of insured premises.
STUDY 6 AVIATION INSURANCE
Includes aircraft (physical damage/hull insurance, liability coverage), for aviation & aerospace risks.
*Aircraft: Any machine capable of deriving support in the atmosphere from reactions with the air (including rockets, not including hovercrafts). Includes general aviation aircraft & airlines (in Canada, # of airlines is limited).
Types of aircraft: Fixed wing (Aerocraft), most single engine/some multi-engine, also Gliders (Sailplanes); Ultra-Light (Microlight); Rotary Wing (Helicopters) & Gyroplanes; Balloons/Airships/Experimental Aircraft.
Types of Landing Gear: Tricycle Formation (Nose Wheel), fixed or retractable; Taildragger Formation (Tail Wheel, older design), fixed or retractable; Floats/Pontoons; Amphibious Design; Skis.
Types of Engines:
Normally aspirated reciprocating (internal combustion) engine (most common).
Turbo (high altitudes):
Turbine engine driven prop (turbo-prop).
Pure turbine (turbo-jet) for most airlines & corporate jets.
Uses of Aircraft: Private business/pleasure/corporate use with professional crew (Industrial Aid), sport (gliding/parachuting), commercial charter, rental, flying training, crop dusting, pipeline/powerline patrol, photography, advertising, survey, fire fighting, construction/logging, air ambulance, traffic reporting, etc.
Aviation Insurance Market: Very small in Canada, few companies; some US/London companies too. Canadian companies don’t write 100% of line, many underwriters share. Airlines Insurers usually include Lloyds and others.
Legislation Affecting Aviation Insurance:
Federal only, Aeronautics Act, Minister of Transport regulates by:
1) Dept. of Transport (DOT/MOT/Transport Canada):
Licences pilots, mechanics, controllers, Certification/Licensing
aircraft.
Aviation Safety (Air Regulations & Air Navigation Orders).
Amount & Form of Liability Insurance for private aircraft.
June 28, 1985, Aeronautics Act, Liability Insurance:
$300,000 X # Passengers for BI/Death each passenger.
To other persons: $100,000 up to 2,300 lbs.
$500,000 2,300-5000 lbs.
$1,000,000 5,000-12,500 lbs.
$2,000,000 12,500-75,000 lbs.
$3,000,000 over 75,000 lbs.
Proof of Insurance to be carried in plane.
Legislation Affecting Aviation Insurance:
2) National Transportation Agency (NTA):
Air Carrier Regulations: For commercial air carriers, amount & form of
insurance.
Minimum Limits of Liability:
BI/Death passengers $300,000 X # seats.
Public $1,000,000 up to 7000 lbs (7500 lbs
rotary wing).
$2,000,000 7000-18000 lbs.
$2,000,000 + $150 per lb excess
weight over 18,000 lbs.
Single limit of liability can be used if greater than above.
Exclusions: War, Hi-Jacking, Noise/Pollution, Radioactive Contamination, Worker’s Compensation Claims, Property in Air Carrier’s Charge.
Additional Exclusions: Coverage restricted to certain aircraft scheduled; if # passengers exceed stated maximum; fraud and misrepresentation; aircraft used for purposes not stated; assumption of liability under contract; chemical drift in spraying operations.
Certificate of Insurance: Submitted to NTA, and notification of cancellation
and changes.
Some commercial operations permitted without a licence (i.e., person flying on
business & being reimbursed by employer, parachuting, towing gliders,
rental, sharing expenses for fuel & fees) but must carry minimum limit of
liability insurance for commercial flying.
3) Canadian Transport Safety Board (CTSB): 1984, Aviation accident investigations, reports to Minister of Transport.
4) US Dept. of Transport (U.S.D. of T.): If planes enter US airspace then
Part 205, Code of Federal Regulations applies. Only for planes in Classes
8 and 9 (airlines, air taxi). All amounts in US funds. Certificate
of Insurance submitted to U.S.D. of T.
Up to 30 seats, 7,500 lbs. BI/PD $75,000 each person /
$2,000,000 each occurrence
BI Passenger $75,000 each person +
$75,000 X 75% # of seats
Up to 60 seats, 18,000 lbs. BI/PD $300,000 each person
/ $2,000,000 each occurrence.
BI Passenger $300,000 each passenger
+ $300,000 X 75% # of seats
Over 60 seats, 18,000 lbs. BI/PD $300,000 each person
/ $20,000,000 each occurrence
BI Passenger $300,000 per person
+ $300,000 X 75% # of seats
Legislation Affecting Aviation Insurance:
5) International Agreements: International flight = any flight where ultimate
destination is in other than the country of origin (even domestic connecting
flight).
Aircraft Policy: No standard form, 5 Parts:
1) Declarations: Name/address Insured, policy period, name/address loss
payees, type/amounts of hull/liability coverages, amount of deductible,
permissible uses of aircraft, describes each aircraft (registration, make,
model, configurations, passenger capacity, year of manufacture), pilots
permitted to fly, previous insurance history, and premium.
2) Insuring Agreements:
Hull: May be ACV or Stated Amount less deductible for total losses;
restrictions for transportation costs, Insured’s own repairs, and
betterments.
i All Risks in flight and not in flight (broadest coverage).
ii All Risks while not in flight (covered if aircraft taxiing, but not landing
or taking off).
iii All Risks while not in motion (on ground, not in motion by own power, laid
up).
iv Named Perils while not in motion and not due to accident (covers fire,
lightning, explosion, etc., rare coverage).
Liability: Most liability insurance is on a single limit basis, +/-
passengers.
Third Party BI to any person not a passenger from Occurrence due to ownership,
maintenance, or use of aircraft.
Property Damage, including loss of use, from Accident due to ownership,
maintenance, or use of aircraft.
Passenger BI from Occurrence due to ownership, maintenance, or use of aircraft,
includes damages to baggage.
Deductibles: Variable: Some policies have deductibles applicable to all losses, others only for partial losses, others have no deductible for certain perils (like lightning).
Duty to Defend: Insurer will defend any BI/PD suit against Insured, even if groundless, false or fraudulent. In addition to policy limits, Insurer pays defense costs, premiums on bonds, and reasonable expenses incurred at Insurer’s request.
3) Definitions:
Insured: Named Insured, plus partners, officers, directors, employees, persons
using aircraft legally. Excludes persons involved in commercial aviation.
Aircraft: Includes equipment and parts temporarily removed.
*In Flight: From time aircraft moves forward to take off until it has completed
the landing run.
*In Motion: When aircraft is in flight, or moving under its own power or from
its momentum in any way.
Moored: Not in motion on water, includes beaching, launching, hauling.
Passenger: Includes crew.
*Accident: Sudden, unusual, unexpected happening attributable to specific act
or omission leading to damage to aircraft and/or property damage.
*Occurrence: Accident, including continuous/repeated conditions, leading to
BI/PD, not expected/intended by Insured.
4) Conditions:
Policy Period & Territory: Within stated period, in Canada; some policies
add continental US (not Alaska) & St. Pierre/Miquelon.
Two or More Aircraft: Policy terms apply separately to each.
Protection of Salvage: Insured must protect from further loss.
Subrogation: Insured must not prejudice subrogation rights.
Auto Reinstatement: Amount of insurance not reduced by loss.
No Return Premium for Loss: Premium fully earned if loss occurs.
Cancellation: Notice period varies 7-30 days, lesser for nonpayment of premiums;
some policies allow a short rate return.
Other Conditions: Like standard liability forms, e.g. fraud,
misrepresentation.
Additional Conditions:
Temporary Use of Substitute Aircraft: Extends cover to similar aircraft up to
30 days after damage to original plane.
Use of Other Aircraft: Non-ownership liability insurance on similar aircraft
for BI/3rd Party Liability to individual Insured.
Automatic Insurance for Newly Acquired Aircraft: 15 days notice is required.
5) Exclusions: No standard form, some examples:
Violation of Air Regulations: Certificate of airworthiness in effect (includes
overweight aircraft). Pilot’s licence, ratings, endorsements
(qualifications). Consumption of alcohol/drugs by pilot within 8 hours of
flying.
Operational Exclusions: Added by endorsement: Record attempts/closed
course racing, crop dusting, dropping parachuters, fire fighting, aerobatics
(usually below 1000 ft), glider/banner towing, exhibitions, etc.
War: Regular war perils; for some policies this only applies to
hull cover.
Wear and Tear.
Tires: Theft of tires still covered.
Excess Passengers: Over maximum stated in Declarations.
Care, Custody, Control: Other property in care of Insured.
Contractual Liability: Liability assumed by Insured under contract, except
airport contract, agreement of temporary storage for defined period, agreement
for minor service, liability which would have attached without contract.
Employees: BI to employees and Worker’s Compensation claims.
Assault/Battery (Intentional losses).
Noise/Pollution (Environmental Exclusion).
Professional Liability: Some policies (e.g. medical services in air
ambulance).
Endorsements: No standard form, some examples:
Pilot Endorsement: Open Pilot Clause for airlines, etc., many pilots used, not
just named individuals; qualified pilots employed (or approved) by Insured.
Mortgage Clause, Breach of Warranty Endorsement: Insurance still valid to
lienholder/lessor even if Insured held accountable for loss.
NTA/U.S.D. of T. Endorsements: If insurance held is less than minimum required
area of use, insurance covers difference, but Insurer can subrogate Insured.
STUDY 7 AVIATION INSURANCE-- UNDERWRITING
& RATING
No published rates, most rating on individual basis; lack of statistical base because of small volume. DOT publishes accident data by type aircraft, use, type licence, regions, and cause, but underwriters use these for reference only.
Application:
Insured:
Commercial: Length of
time in business, background of ownership, financial viability, record of
losses.
Private:
Occupation, record of Losses.
Aircraft: List of all aircraft, including registration letters, make, model,
year, landing configuration, value, max. # passengers/crew, amount liens, limit
of liability.
Usage: Commercial: List of air carrier licences, operations conducted, #
hours/miles annual use.
Private: Any services for $, aerobatics, parachuting, etc.
Pilots: Commercial: May be unnamed pilots.
Private: Pilot report/history forms for each (name, age, type licence,
endorsements, when/where course taken, employment record, flying violations
record, accident record, recurrent training, # hours flown).
Environment: Base location & details of airport/strips; hangared or tied
down; flying to remote areas & outside America.
Effect on Rating:
Insured: Underwriter may decline if negative view of Insured; may charge higher
premium for new venture; may add occupational surcharges.
Aircraft: Old: Rating may be higher or risk declined, as spare parts
rare. Component Parts Endorsement can be used to set a maximum limit of
insurance on each component (i.e., engine, fuselage, wings, etc.), rare.
Type: Rating higher or risk declined for certain types (e.g. helicopters, ultra-lights).
Purpose-Built Aircraft: Rating higher or risk declined (e.g. plane built for
aerobatics). Configurations: Rating higher or risk declined for planes on
floats/amphibious planes. Make/Model: Rating based on statistics on the
basis of # accidents per 100,000 hours flown.
Usage: Prime factor in rate setting (statistics for # accidents per 100,000
hours flown by type of operation, and fatal accident rate per year).
Pilots: Rating higher for less experienced pilots (student rate higher).
If more than 1 pilot, rating by most inexperienced pilot. Rating higher
for greater number of pilots. Age does not usually affect rating
(surcharge for very old pilots). Flying record considered
(accidents/violations). Rating lower for greater number of pilot proficiency
tests.
Environment: Higher rates for far north or obsolete location of base; rates
based on statistics for location of base and areas flown.
Terms of Coverage:
Hull Rate: Applicable to highest value insured (formerly different values
if on skis, wheels, floats). Reporting policies = Rate per day.
Deductibles: Greater for more valuable aircraft (airlines $500,000 to
$1,000,000, except total/constructive total losses. No deductible on some
risks (corporate small jets). Some policies have a varying deductible
(different for plane in motion, moored, etc.). Private planes: Deductible
may be $250 not-in-motion/$1000 in-motion (ultra-lights have a higher
not-in-motion deductible).
Liability Premium: Third Party BI/PD + Passenger BI, rate per seat or rate per
revenue passenger mile (rpm).
Optional Endorsements & Other Coverages:
Lay-Up Endorsement: Premium returned at expiry for periods of lay-up (minimum
30, 60, 90 days), not laid up due to loss. Only a percentage of premium
is returned (still covered for ground risks). Returns limited or
eliminated if renewal insurance not with the same Insurer.
Knowledge/Consent Endorsement: Protects Insured only; Insured not prejudiced if
third party does some act that would void policy, as long as action not due to
the Insured and beyond his control.
NCB/PCOR (No Claims Bonus/Profit Sharing Endorsements): If an Insured has a
claim-free year on all aircraft, 5-12 % of the hull premium returned.
Spare Parts Endorsement: Covers spare parts supply for ground risks.
Premium Insurance (UPI): In case of total loss, hull premium returned pro
rata.
Contingent Employers Liability Endorsement: Covers liability of Insured for
injury to employees not covered by Worker’s Compensation.
Admitted Liability (Guest Voluntary Compensation, GVC, GVS): Insurer pays
stated amounts for death/dismemberment/total disability without proof of
liability, at Insured’s request (Industrial Aid Risks).
Baggage Liability: Modest limits; some exclusions; commercial risks.
Cargo Liability: Full legal liability (not necessarily from Accident) for whole
trip, not including damage/loss from delay, employee infidelity, to certain
cargo.
Cross Liability Endorsement: Policy responds for claim by 1 Insured against
another Insured under same policy.
Contractual Liability/Waivers of Subrogation.
Additional Insureds.
Loss of Use.
Non-Ownership Liability: Insures operation without ownership (individual,
corporate or commercial forms), excess to other insurance.
AVIATION INSURANCE - UNDERWRITING & RATING:
Aviation General Liabilities (Exposures):
Ground Operations:
Premises & Operations Liability:
Airport Liability: Most airports are federally owned and are
self-insured. Private airports need insurance (Aviation Liability).
Hazards include failure to upkeep runways, navigation, communications.
Airport Tenants: Includes airlines, operators who rent/own property at an
airport. Policy Form: Like general liability form but tailored for
aviation. Liability of Insured from ownership, maintenance, use of stated
premises.
Exclusions:
Property in care/custody/control of Insured.
Nuclear energy liability.
Products/completed operations.
Operation of licensed vehicles.
Employer’s liability.
Contractual liability.
Airshows/meets for accident in grandstands/bleachers.
Elevators/escalators.
Alterations/construction/demolition.
Environmental disturbance.
Aircraft being refueled.
Hangarkeeper’s Liability: For property in care/custody/control of Insured;
moderate deductible; fire hazard included; type & number of aircraft stored
& worked on.
Exclusions:
Personal effects.
Aircraft of Insured.
Contractual liability.
Actions of Insured.
Loss/damage while aircraft in flight (In-Flight policy available for much
higher premium, to cover for test-flights, etc.).
Products/Completed Operations Liability: For sales/service companies &
manufacturers. Hazards:
Sale of new aircraft, rating low, dealer has few responsibilities.
Sale of used aircraft, rating high.
Repair/service of aircraft, rating high.
Sale of aircraft, parts not installed, rating moderate.
Aircraft painting, rating low.
Sale of gas & oil, rating moderate.
Sale of food & drink, rating low.
Rating: By Insured’s gross receipts, per hazard.
Exclusions: Contractual liability, Worker’s Compensation, Property in
Care/Custody/Control of Insured.
Satellites: Number of commercially owned satellites constantly
increasing.
Coverage: 3 Phases:
1) Launch: Most hazardous; provided by government vehicle, not guaranteed
(hold-harmless agreement, no subrogation).
2) Early Life: 1st 6 months.
3) Late Life: 6 months to 7-10 years.
No Deductible.
Coverage: Physical loss including failure to perform (cause impossible to
determine since in space).
Incentive Insurance: Ensures manufacturer receives incentives as satellite
completes its 3 phases.
Liability Insurance: BI/PD in crash to earth, not between 2 satellites.
STUDY 8 AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE-- SELECTED COVERAGES
Crop Hail Insurance:
Hail occurs when 2 weather fronts meet (warm and cold), variable size, can
occur anywhere. All kinds of crops can be covered (usually wheat).
History:

Underwriting: Carriers include stock companies, cooperatives, associations (municipal/provincial govt.). Stock companies write directly or through Managing General Agents (MGA’s). There are no longer any mutual companies handling hail insurance.
Insurable interest (includes rental of land ‘share of crop’ but not cash
rental).
Liability commences the day after application mailed to Insurer; payment must
accompany application.
Cancellation by written request of Insured (Insurer cannot cancel once
accepted).
Valued policy: Specified amount per acre. No Coinsurance requirement
(difficult to assess value of crop before harvested).
Facultative Reinsurance is necessary to protect Insurer as losses are cyclic
(good and bad years) + adequate distribution of risk.
Types of Policy: Full Cover, 10% Deductible, 25% Deductible. These may be
modified by Optional Disappearing Deductible endorsement (deductible higher as
amount of loss higher).
Rating: Based on territory & amount of insurance per acre; rates set for
each season.
Crop Hail Insurance:
Loss reporting required in writing within 3 days. Loss Adjustment: Use
‘100 Plant Count System’ to determine loss; Proof of Loss form required;
Arbitration is possible (rare). Percentage of loss determined within 30
days.
Changes: Expiry date now October 01.
Cut-Grain endorsement covers crops already cut, waiting for collection (lying
in windrow or swath).
Harvesting, Allowance endorsement (no longer in use): Where loss exceeds 70%,
covers extra 10% for harvesting damaged crop. Today, insurers pay for
total loss if loss exceeds 85 or 90%.
Livestock Mortality Insurance:
Term Life insurance (all risks of mortality) on animals; death from disease,
accidental injury, fire, lightning, windstorm, and authorized destruction for
humane reasons - while in transit in North America.
Enhancements of Coverage:
Infertility Coverage: Animal doesn’t die, but economic loss from infertility
(varying coverages available).
Semen Suitability Coverage: For artificial insemination programs, if found
unsuitable for this purpose.
Economic Slaughter Coverage: Economic loss from inability to perform (animal
becomes property of insurer for ‘salvage’).
Exclusions: Common Insurance Exclusions, plus:
1 Surgery, other than to save animal’s life.
2 Administration of drugs/medicine, other than by vet.
3 Mysterious disappearance/escape.
4 Intentional slaughter.
5 Malicious/willful/intentional acts of Insured.
6 Voluntary parting with title or possession.
Requirements in case of sickness or injury: Licensed Veterinarian must attend
at Insured’s expense & immediate notice to Insurer.
Requirements in case of loss: Immediate notice & Vet. report.
Coverage for death only, not minor injury/depreciation/failure to perform.
Livestock destroyed with Insurer’s permission only.
Underwriting: Maximum & minimum age limits, prohibited & uninsurable
lists, Declaration of Health, limits of liability (ACV or money invested).
STUDY 9 MISC. COVERAGES
Contingency Risks Insurance: Insurance for unusual exposures; specially designed; not otherwise covered by common types of insurance. Many different forms, for risks with established statistical bases. For risks fortuitous to Insured; contract of Indemnity.
1) Event Cancellation Insurance: Organizers have insurable interest in their
events; for cancellation, curtailment, postponement of insured event from cause
beyond control of Insured or participants.
Loss (less costs recouped or avoided as a result of cancellation) possible
from:
- Non-recoverable costs before event or before loss
- Sums Insured obliged by contract to pay to others, whether event takes place or not
- Gross receipts on advance ticket sales
- Advertising or sponsorship revenue
- Television rights
- Other revenues secured contractually before event
Loss from television transmission failure (for TV
advertising of event, partial or complete) covered by extension. Also
covers physical damage to signs used in telecast.
Exclusions (*some waived for extra premium):
- Any matter, fact, circumstance existing at policy inception.
- Failure of event because organizers were unable to make necessary preliminary arrangements or secure necessary contracts.
- Reasons within control of organizers or participants.
- *Withdrawal of participants by their own choice.
- *Failure of individual participants to appear.
- Lack of support or financial causes.
- Breach of contract.
- *War and Civil War.
- Failure of organizers or their agent to obtain television coverage. Failure or reduction of television transmission by decision of producers, unless interrupted by important news.
- *Satellite failure, preventing transmission to other countries.
- *Failure of transmission in country other than country of location of event.
- Refusal of access to transmission signals.
- Consequential loss, e.g. refusal of sponsor to renew contract.
Contingency Risks Insurance:
2) Nonappearance Insurance: Individual participants may sustain a loss by their
failure to appear (indemnity agreements, appearance fees); a separate policy
written to indemnify participants (own loss and liability) for failure to
appear from circumstances beyond their control.
3) Breakdown of Transmission Insurance: Purchased by agency providing
audio/visual signals for advertising for special events; covers own costs and
liability to organizers of events in case of failure beyond agency’s control.
4) Death & Disgrace Insurance: Covers organization for loss when their
spokesperson(s) dies suddenly or is found to be involved in criminal or
disgraceful situation (scandal), forcing advertising campaign to be cancelled.
5) Prize Indemnity Insurance: Indemnifies sponsor if prize claimed (available
only for prizes which may or may not be claimed--element of chance).
E.g., Hole-In-One Insurance: For golf-tournaments, prize offered to 1st player
to get hole-in-one; insurance indemnifies sponsor if someone succeeds.
E.g., Fishing Derbies.
Warranty Insurance: ‘Warranty’ here means a written guarantee or
assurance that a product is fit for its intended use. The warranty
protects the purchaser of a product for defects for a specified time after
purchase. Extended warranties (from manufacturer or third party, i.e.,
insurer) continue to protect the purchaser after the basic manufacturer’s
warranty expires. Some provinces regulate extended warranties (considered
a form of insurance). 2 forms:
1. Financial Guarantee: Party that issues extended warranty buys performance
bond from Insurer. Bond obligates Insurer to pay legitimate claims
against warranty--only if issuer cannot because of financial failure.
2. Extended Warranty Purchased Directly from Insurer: Insurer collects premium
from purchaser, and pays any claims against warranty.
Coverage: May duplicate basic warranty and extend time, or may alter
protection afforded. Usually, extended warranties offer narrower
protection. Some extended warranties offer Enhancements (like auto
extended warranties include sub-limits for towing, rental, travelling
expenses).
Exclusions:
- Wear and Tear
- Misuse of Object
- Abuse of Object
- Bylaws
Difference in Conditions Insurance (DIC): Customizes coverage of property policies to include some types of property or risks of loss. Less common in Canada than in US; here, it is easier to modify conventional policies for unusual requirements. DIC’s used for large exposures, and for global insurance programs (adapting coverage to each subsidiary). No standard forms, similar to umbrella liability policy, each contract custom designed. One form is a Difference in Limits Policy (DIL): policy only alters amounts of policy limits.
Difference in Conditions Insurance (DIC):
Coverage: Usually for catastrophic loss, large deductibles; named perils
or all-risks; highly variable.
Exclusions: Supplements other insurance, and so excludes loss caused by
perils covered by other property policies. Also Excludes:
TYPES OF PROPERTY PERILS
- Money, currency, evidence of debt or title, notes, securities
- Jewellery, precious stones or metals, furs, fine arts
- Animals, plants
- Construction, transit
- Watercraft afloat, aircraft
- Underground property
- Piers, wharves, docks, bulkheads, dams
- Property sold under conditional sale agreements
- Contamination, gradual deterioration, wear and tear, moths, vermin, inherent vice
- Error in design or processing, faulty workmanship or materials
- Employee dishonesty
- Shrinkage, evaporation, loss of weight, dampness of atmosphere, extremes or changes in temperature, changes in flavour, colour, texture
- Normal settling, shrinkage, expansion of foundations, walls, floors, ceilings
- Enforcement of law regulating construction, repair, demolition
- Unexplained loss, mysterious disappearance
- War, nuclear hazards
- Often excluded or limited: Flood, earthquake
Underwriting: Take into account physical characteristics, topography, construction, condition, security, exposure to flood/earthquake if covered. Linesetting: Limit of Liability = ‘Line’. Underwriters try to determine Probable Maximum Loss (PML).
Entertainment Insurance: Multi-faceted business, productions are major financial investments; cancellation or delay = financial loss. Insurance can protect investors & recover lost funds spent on cancelled project or resume production. Anyone who has financial (insurable) interest in a project can insure.
Coverages:
- Illness or Injury of Cast & Crew: Continuing expenses until production resumes; may be extended to animals.
- Negative Film & ‘Faulty Coverage’: Pays for re-shooting lost/damaged footage.
- Props, Sets, & Wardrobe: Property coverage & third party liability coverage.
- Misc. Equipment: Property coverage & third party liability coverage, specified perils, only for leased/borrowed equipment.
- Third Party Property Damage: Liability Insurance, for property of others.
- Extra Expense: Extra expense to complete principal photography if production interrupted/postponed by damage to property/premises.
- Office Contents: Property Insurance for business property.
THEATRICAL PRODUCTIONS:
- Theatrical Property: All Risks property coverage.
- Extra Expense: Covers extra expense from delay due to damages.
- Actor’s Equity: Personal property coverage.
- Catastrophic or Accident Coverage: Covers non-recoverable costs.
SPECIAL COVERAGES (ENTERTAINMENT INDUSTRY AS WHOLE):
1 Errors & Omissions Insurance: Invasion of privacy, copyright
infringement, libel, slander.
2 Kidnap & Ransom & Extortion Insurance: Abductions, extortions, threat
or actual.
Nuclear Energy Insurance:
Nuclear Insurance Association of Canada (NIAC) insures almost all nuclear
risks; excluded from other policies. NIAC (1957) is a pool (association)
of domestic & foreign insurers.
Liability Insurance for Risks with Nuclear Energy Exposure: The Nuclear
Liability Act (1961) requires nuclear power plants to have at least $75M
liability limits. Lower limits for lesser risks (e.g., universities) set
by Atomic Energy Control Board.
1. Operator’s Form: Legal liability for operators of nuclear installations;
legal liability for BI/PD from nuclear incident, including radioactive
contamination. Excludes: Nuclear weapons, war risks, radiation emitted
during normal operation, nuclear material at other location. Claim filed
within 10 years after expiry.
2. Facility Form: Not for working reactors, but those working with nuclear
energy (e.g. manufacturers of fuel bundles for reactor). Products
liability BI/PD, transportation. Excludes manufacturing, handling, use at
described location, nuclear weapons, war risks, ionizing radiation. Claim
filed within 2 years after expiry.
3. Suppliers’ and Transporters’ Form: Reinserts coverage excluded in commercial
general liability (CGL) form. Legal liability for BI/PD from nuclear
energy hazard. Limits $1M-$75M. Excludes: Nuclear weapon, war
risks, prescribed substances. Claim filed within 2 years after expiry.
Property Insurance for Risks with Nuclear Energy Exposure: Nuclear Energy Physical Damage Form (NIAC): Direct physical loss/damage from radioactive contamination and all risks. Excludes loss from gradual accumulation of radioactive contamination. Greater property values of nuclear power plants = higher limits of liability; generally $60M-$1B.
Credit Insurance: Credit is a necessity; for sellers to be competitive, they need to offer flexible terms of payment to a buyer; buyer may fail to pay debt, though.
Credit Risk: Manufacturer retains insurable interest if product sold on credit, exposure to loss in accounts receivable.
To reduce credit risk: choose payment method favourable to seller, or seller can demand letter of credit, or purchase Credit Insurance. Credit Insurance guarantees to seller of goods or services that it will be paid for goods sold or services rendered.
Benefits of Credit Insurance:
- Protects and stabilizes profits by guarding against abnormal credit losses beyond seller’s control.
- Allows seller to be competitive, + offer flexible terms of credit.
- Protects seller’s cash flow, substitutes certainty of predictable insurance premium for uncertain payment of debts.
- Allows seller to extend credit, reaching new buyers.
- Aids seller in borrowing, collateral for loans.
Coverage: Loss arising from seller’s inability to collect accounts receivable from buyers as a result of commercial risk or political risk beyond Insured’s control. Commercial Risk includes insolvency of buyer or bank, default of buyer, repudiation by buyer. Political Risk includes transfer difficulties or blockage of funds, war, cancellation/nonrenewal of import or export permits, foreign government action.
Exclusions: Trade disputes between seller & buyer, risks normally covered by other commercial policies. Usually, coverage only for 90% of claim.
Underwriting: Take into account seller’s credit procedures, credit period, methods of payment, buyer’s financial condition, location, number.
Personal Legal Expenses Insurance: Pays reasonable legal expenses incurred with Insurer’s consent in most civil disputes; paid on behalf of Insured (not reimbursed). Also pays for expenses incurred in criminal disputes if Insured acquitted or charges dropped. All Risks Coverage.
Excludes: Business activity, exposure covered by other policy, fines & penalties, costs incurred without Insurer’s prior consent, disputes existing at inception of coverage, disputes between Insureds, matrimonial disputes in 1st year of policy (sub-limit from then on), disputes less than $500, non-contentious legal matters (e.g., drawing up a will).
Limits: Per claim and aggregate amount per term and sub-limits for certain types of claims; for actions in Canada only; no commercial coverage yet.
Legal Fund: Alternative to this insurance; Individuals pay into fund which protects its individual members when required (until fund exhausted).
STUDY 10 TRAVEL HEALTH INSURANCE
Universal Health Care: Canadians within Canada have comprehensive health care provided by the government and paid by taxes.
GHIPs: Government Health Insurance Plans; this is the Government Health Insurance provided for Canadians while in Canada; each province has its own plan, but Canadians travelling between provinces are covered by reciprocal agreements. GHIP’s regulated by federal Canada Health Act so all GHIP’s are similar; some differences exist between GHIP’s in different provinces.
Eligibility: OHIP coverage restricted to permanent residents of Ontario with valid OHIP card. A person absent from the province for 183 days in a 12 month period loses Eligibility subject to a 3 month waiting period.
Services Covered (Inside Canada): For medically necessary services only (services for cosmetic surgery, for example would be excluded):
Doctors: Fees covered according to Schedule of Benefits (no extra-billing, but doctors can charge patient for services not included in Schedule).
Hospitals: OHIP covers cost of standard ward bed, physician care, nursing care, and diagnostics.
Podiatrists, Chiropractors, Osteopaths: OHIP pays only part of these costs.
Physiotherapy: In hospital, all costs covered. Outside of hospital, very few clinics covered.
Dental Care: Coverage limited to certain types of dental surgery performed in hospital.
Optometrists: Only vision tests covered.
Ambulance Services: Air Ambulance & Land Ambulance service covered for medically necessary trip only, subject to deductible; no deductible for patient transfer between facilities.
Services Covered (Outside Canada): Far more restrictive:
Emergency Services: Covered with limitations, these are services for acute, unexpected condition, illness or injury that requires immediate treatment. Physician costs limited to what those services would cost in Ontario. Emergency Inpatient Hospital services limited to $400 per day. Emergency Outpatient Hospital services limited to $50 per day ($210 for dialysis).
Elective Services: Not Covered (except in rare cases where services not available in Ontario for new recognized medical procedure, and patient obtains approval from Ministry).
Need for Travel Health Insurance: All extra costs for services outside Canada must be paid by the patient—hence the need for Travel Health Insurance. This insurance may also cover other charges not medical in nature (forfeited air tickets, returning an automobile home, etc.)
Travel Health Insurance: Not comprehensive coverage—not as much protection that a GHIP provides while resident is in Canada. Coverage is limited (maximum payouts, restricted definitions, exclusions of services & events). Covers only unexpected events. Covers only medical emergencies. Coverage is Excess to GHIP and other existing insurance policies; pays only after primary insurance exhausted. Coverage is Primary in absence of other insurance.
Travel Health Insurance, Definition: Limited insurance for eligible expenses incurred as a result of illness or injury in unexpected medical emergencies while travelling.
Regulation: Travel Health Insurance cannot replace GHIP. Policies regulated by Insurance Acts. In most provinces, brokers & agents must demonstrate knowledge of Travel Health Insurance to obtain licence.
Types of Travel Health Insurance:
1. Per Trip Policy: Coverage for 1 trip only; no return and exit from province;
policy terms of 1 day to 1 year; for holiday, insureds who travel infrequently;
Insured must be eligible for GHIP.
2. Multiple Trip Policy: For frequent travellers; policy period 1 year;
restricted number of days per trip.
3. Primary Insurance Policy: For Insureds not eligible for GHIP. May
replace coverage provided by GHIP—second Travel Health Insurance policy needed
to provide excess coverage.
Application: Considerable onus on Insured in most cases to buy suitable coverage
and review policy once received.
Misrepresentation voids the policy; 3 Types:
1. Telephone Applications: Only minimal information required by insurer.
2. Pre-Approved Self-Write Applications: May also include health information.
3. Applications Subject to Underwriting Approval: Rare: Include more detailed
information; approved if applicant passes scrutiny.
Policy: No standard wordings; common definitions:
- Accident: Unintentional, sudden, fortuitous and unforeseeable event due exclusively to external cause of violent nature and inflicting, directly and independently of all other causes, BI.
- Injury: Sudden BI directly caused by accidental means which is independent of sickness & other causes.
- Sickness: Illness or disease which results in Emergency treatment or care.
- Illness: Sickness or disease first manifesting itself while policy in force.
- Medical Emergency: Unexpected or unforeseeable sickness or injury which requires immediate non-discretionary medical attention, treatment or care.
- You and Your (Insured): Any person who is named on the application eligible for coverage.
- Insured Person: Person named in application, Spouse and Dependent Children if enrolled under Family Coverage.
- Dependent: Insured’s unmarried children under 21 (& students under 25-26) who are financially dependent upon the Insured.
- Extended Family or Relative: Insured’s children of any age, spouse, parents, brothers & sisters (in some cases others).
- Grandchildren: Children or step-children of Insured’s son, daughter, son-in-law, daughter-in-law, step-son or step-daughter.
- Hospital: General active treatment hospital. Other definitions exist.
- Inpatient: Patient confined to hospital for 24+ hours on recommendation of attending physician.
- Physician: Duly qualified doctor of medicine entitled under law where services rendered to practice medicine or surgery without restriction.
Usual, Customary and Reasonable Expenses: Services covered must be usual (usual charge of Provider), customary (within range of usual charge of Providers in that area and expertise), or reasonable (justifiable charges for particular case, according to Provider’s professional association).
Optional Extension Period: Number of days coverage added to existing policy period.
Automatic Extension: When Insured hospitalized for medical emergency on return date, coverage remains in force until 72 hours after discharge.
Limits of Insurance: Variety of limits exist: Aggregate Limit (maximum
amount insurer will pay for all losses), Limits for Individual Coverages,
policy may be Unlimited for certain coverages.
Coverages (Benefits):
Accident & Baggage: May be provided on Primary basis.
Hospital Expenses: Covered expenses vary.
Physicians’ Charges: Reasonable & customary charges covered.
Paramedical Services: Costs (physiotherapist, chiropractor, osteopath, chiropodist, podiatrist, naturopath) may be covered to a set limit.
Private Registered Nurse: Coverage may be restricted to expenses while Insured in hospital; may be limit $5,000-$10,000. Service provided only on order of physician.
Special Treatments: Coverage may include cost of blood, oxygen & specialized treatments in hospital.
Diagnostic Services: Laboratory tests & X-rays covered.
Medical Appliances: Coverage specified for rental of hospital bed, wheelchair, crutches, etc.
Land Ambulance: Coverage includes expense of local, licenced ambulance to nearest qualified or eligible medical facility.
Air Ambulance: May cover expense of evacuating insured by air between 2 hospitals or to Canadian hospital (by regular commercial flight or specially equipped plane) with approval of Emergency Assistance service.
Prescription Drugs: Some types of drugs covered with many limits and exclusions.
Dental: Some dental work covered with many limits and exclusions.
Repatriation (Emergency Return Home): Covers air transport of Insured home for immediate medical attention, ordered by physician.
Return of Deceased: In event of death, covers disposition of remains with many limits.
Return of Vehicle: Various costs of retrieving vehicle are covered with limits.
Return of Accommodation Fees: Covers costs of accommodation paid by Insured but forfeited when forced to return because of illness or injury, with limits.
Return to Attend Family Member: Covers costs of returning home to attend the funeral of family member or be with family member who is critically ill.
Visit to Bedside: Covers cost of transport of family member to visit hospital or to identify remains, where Insured critically ill or dies.
Meals and Accommodation: Covers expenses of delayed return due to illness or injury.
Incidental Hospital Expenses: Covers incidental expenses usual to hospital stay (long-distance calls, television, etc.)
Emergency Assistance: “Emergency Assistance Benefit” provided by insurer usually contracted to private assistance company; service used to locate nearest appropriate medical facility, physician, etc.; may also penalize insured for failing to comply with provisions of benefit.
General Terms (Conditions, Provisions): Common provisions exist for
Excess/Primary provision, eligibility of GHIP, indemnity, notice of claim,
payment of benefits, reasonable & customary charges, transfer of policy,
misrepresentation, subrogation, etc.
Termination: Coverage ceases on the earliest of (i) last day for which
insurance purchased, unless automatically extended, (ii) date Insured ceases to
be eligible for coverage.
Start & End of Trip: Trip begins on departure date shown on
application. Trip ends on the earlier date of return home or expiry date.
Currency: Amounts payable are stated in either Canadian or US currency.
Interest: No sum payment will carry interest.
Limitations & Exclusions: The aggregate policy limit may be shown
here. As well:
Pre-Existing Conditions: Most policies exclude pre-existing conditions; health
history affects coverage. Current and past health of applicant will
determine whether coverage is provided either in part or at all; or on claims
arising from pre-existing condition.
Country of Destination: Some countries may be excluded.
Elective Treatment: Only medical emergencies are covered.
Specified Medical Procedures: Some procedures will be specifically excluded
(like cataract surgery, cardiac surgery, etc.) depending on policy.
Age: This exclusion may be used to delete coverage in total or in part for
those not meeting the age requirements.
Travel Contrary to Medical Advice: Insured travels against the advice of a
physician.
Intent: Planned medical treatment is not covered.
Pregnancy: May be partial coverage for charges associated with pregnancy with
limits.
Unapproved Facility: Not covered.
Failure to Follow Instructions: Insured fails to follow advice of assistance
service.
Specific Conditions or Diseases: Specifies certain diseases that are excluded.
Self-Inflicted Injury: Includes suicide, attempted suicide, other injuries.
Abuse/Misuse: Of medication, alcohol, toxic substances, drugs.
Impaired Driving, Speed, Endurance Contests: Expenses arising from these not
covered.
Criminal Acts: Expenses arising from these not covered.
War: Common War Perils excluded.
Participation in Professional Sports: Most insurers exclude this.
Mental or Nervous Breakdown: Usually excluded.
Eyeglasses, Hearing Aids, Prosthetic Devices: All excluded.
Non-Commercial Air travel: Only commercial flights or air ambulance are
covered.
Experimental, Investigatory Services: Expenses arising from these not covered.
Unless Pre-Approved: List of expenses covered only with prior approval.
GHIP Contravention: Expenses that contravene coverage allowed by GHIP excluded.
GHIP Covered Expenses: If covered by GHIP, no coverage here.
Deductibles: Listed here are relevant deductibles for policy or parts of coverage, in $ or % form.
Underwriting: Underwriting necessary for policies that offer very broad coverage. Most rely on policy wordings to limit risk. Coverage/underwriting must be provided quickly because Travel Health Insurance is often an afterthought. The underwriter needs to determine the applicant’s health, length of trip, country of destination, etc.
Claims: Policy/certificate will usually contain a claim form; once signed by Insured, the insurer is authorized to: obtain medical records, claim under GHIP, check GHIP eligibility, obtain from anyone any information needed to process the claim, provide health-care information to third party health-care provider. GHIP authorized to collect information regarding the claim. Authorizations are subject to the Freedom of Information Act and the Health Insurance Act. Insurer will request all relevant (original) documents to support the claim, and other information relating to the claim.
Subrogation: The Canadian Life & Health Insurance Association (CLHIA) helps co-ordinate efforts to settle claims where more than one source of coverage exists.
EXAM TIME--GOOD LUCK!!!
Michael B. Downer, A.A., B.Sc., C.I.P., President
Marine Insurance Services E-Mail
downer@marineinsureservices.com
HOME
MEMBERS: IIC, OMSA,
ABYC, IAMI
A Division of 1134935 Ontario Limited